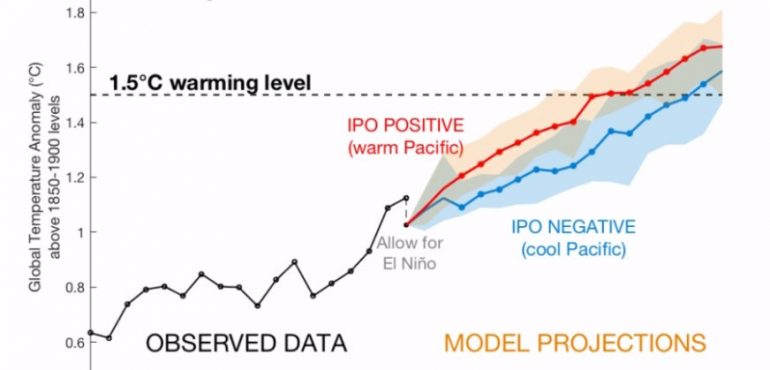
Global temperatures could break through the 1.5°C barrier negotiated at the Paris conference as early as 2026 if a slow-moving, natural climate driver known as the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation (IPO) has, as suspected, moved into a positive phase. New research published in Geophysical Research Letters by University of Melbourne scientists at the ARC Centre of…
Read more
Paris 1.5°C target may be smashed by 2026