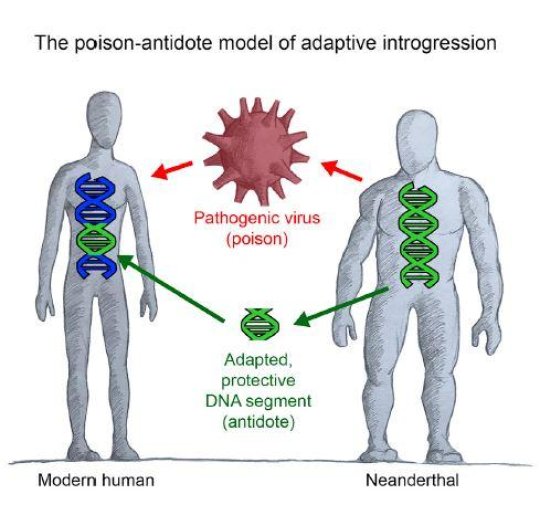
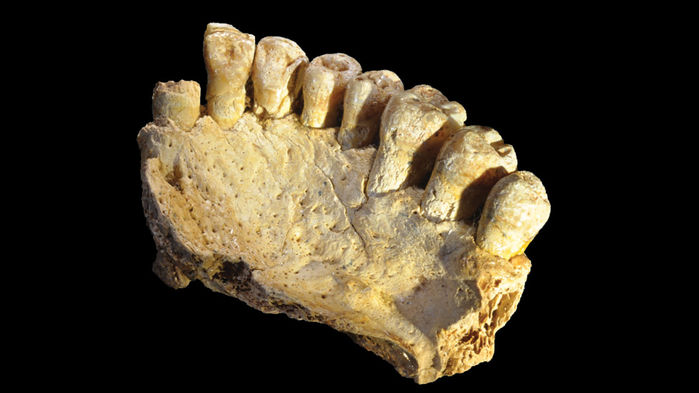
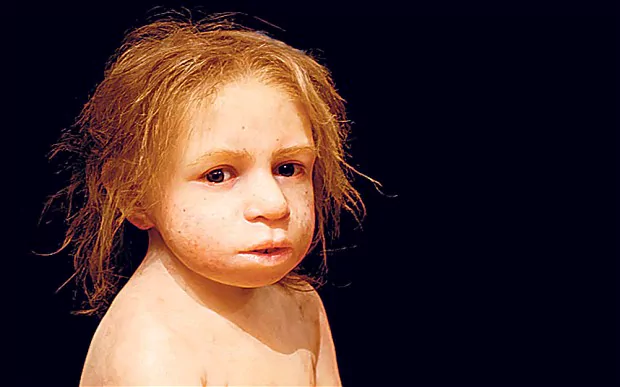
By combining deep learning algorithms and statistical methods, investigators from the Institute of Evolutionary Biology (IBE), the Centro Nacional de Análisis Genómico (CNAG-CRG) of the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) and the Institute of Genomics at the University of Tartu have identified, in the genome of Asian individuals, the footprint of a new hominid who…
Read more
Artificial intelligence applied to the genome identifies an unknown human ancestor