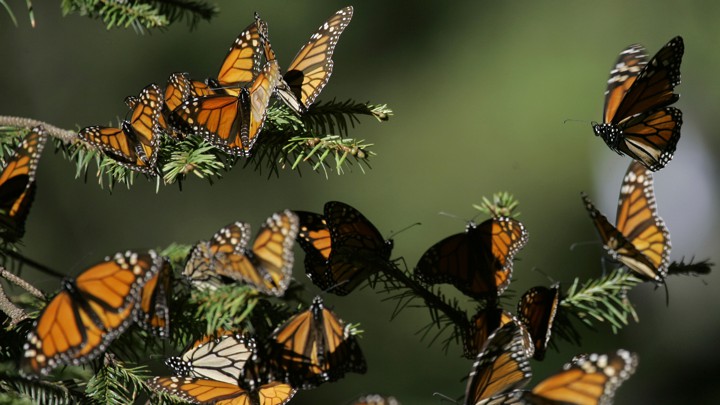
For monarch butterflies in the eastern United States, life revolves around milkweed, a group of about 100 plants in the genus Asclepius that provide food, shelter and nectar for the iconic insects. During their annual migration to the their overwintering sites in the mountains of Mexico, millions of the butterflies float from milkweed to milkweed…
Read more
How This Popular Garden Plant May Spread Parasites That Harm Monarchs