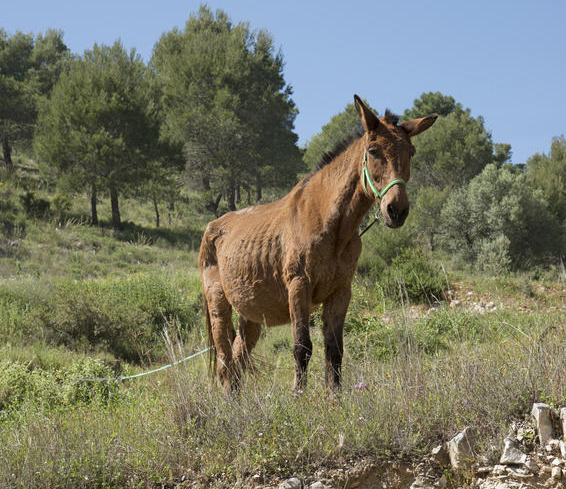
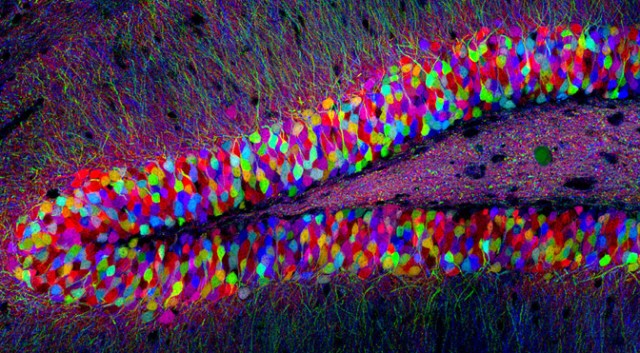
MIT researchers have shown, for the first time ever, that memories are stored in specific brain cells. By triggering a small cluster of neurons, the researchers were able to force the subject to recall a specific memory. By removing these neurons, the subject would lose that memory. As you can imagine, the trick here is…
Read more
MIT discovers the location of memories: Individual neurons